Overview
This guide provides step-by-step instructions on how to create, configure, and execute custom Lambda tasks using the Carrier platform. Lambda tasks allow you to automate reporting, post-processing, and testing functionalities on the Carrier platform to optimize and streamline performance testing workflows.
The guide also covers how you can utilize these custom tasks to automate repetitive processes, like weekly reporting, anomaly detection, and script generation, which ultimately saves time and effort. Additional details about Lambda usage can be found here.
Why Use Lambda Tasks in Carrier?
Lambda tasks provide automation capabilities for complex performance testing workflows, helping performance engineers to:
- Reduce manual reporting: Automate weekly, monthly, or ad-hoc reports summarizing test results.
- Detect performance anomalies: Use automation to detect anomalies or unexpected behaviors in test results, such as response time spikes or throughput drops.
- Automate script generation: Automatically generate or update test scripts from HAR files or user flows.
- Integrate CI/CD workflows: Automate performance test setup, execution, and result post-processing within CI/CD pipelines.
By using Lambda functions in Carrier, you save time, reduce manual intervention, and ensure consistency in your performance testing processes.
Step-by-Step Instructions for Setting Up and Running Lambda Tasks in Carrier
Step 1: Setting Up Lambda Function Handlers
The Lambda function handler is the method in your function code that processes events. When your function is invoked, Lambda runs the handler method. The handler function follows this general syntax in Python:
1
2
3
def handler_name(event, context):
...
return some_value
You need to specify the Lambda handler during task creation in Carrier. For example, if your handler is lambda_handler in a file named lambda_function.py, the handler is referred to as lambda_function.lambda_handler.
Example: Reading Task Parameters from the Event Object
Carrier will pass task-specific parameters via the event object:
1
2
3
4
5
6
def lambda_handler(event, context):
report_id = event.get("report_id")
project_id = event.get("project_id")
token = event.get("token")
...
return some_value
This enables you to access key task parameters like report IDs, tokens, and custom task variables.
Step 2: Packaging and Preparing Lambda for Deployment
If your Lambda function uses non-standard Python libraries, you’ll need to include them in the requirements.txt file. Carrier uses the same packaging rules as Lambda.
Building the Lambda Function with Docker
Use Docker to package your Lambda function with its dependencies:
If you want to use another Python version you could find it here getcarrier/lambda
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
#!/bin/bash
mkdir lambda
docker run --rm -v "$PWD":/var/task lambci/lambda:build-python3.7 pip install -r requirements.txt -t /var/task/lambda
cp -r perfreporter lambda/perfreporter
cp -r templates lambda/templates
cp lambda_handler.py lambda/lambda_handler.py
cd lambda
zip function.zip -r .
cp function.zip ../
cd ..
rm -rf lambda
For example, here is a docker run command for Python 3.11:
Here you can find a list with diferent Python builder images:
Choose the version that suits the requirements of your task and satisfies the architecture of the machine on which the build is executed
- getcarrier/lambda:python3.11-build
- getcarrier/lambda:python3.11-build-x86_64
- getcarrier/lambda:python3.11-build-arm64
- getcarrier/lambda:python3.10-build
- getcarrier/lambda:python3.10-build-x86_64
- getcarrier/lambda:python3.10-build-arm64
- lambci/lambda:build-python3.8
- lambci/lambda:build-python3.7
- lambci/lambda:build-python3.6
- lambci/lambda:build-python2.7
Step 3: Creating Lambda Task in Carrier
Once the Lambda function is packaged, you can create the task in Carrier:
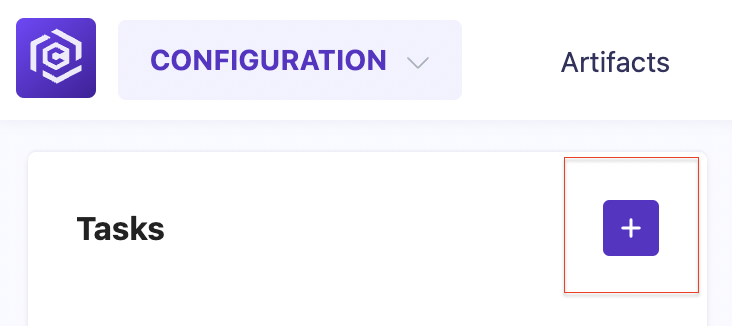
Go to the Configuration Section: Navigate to the “Tasks” subsection in the Carrier UI.
![Tasks section]()
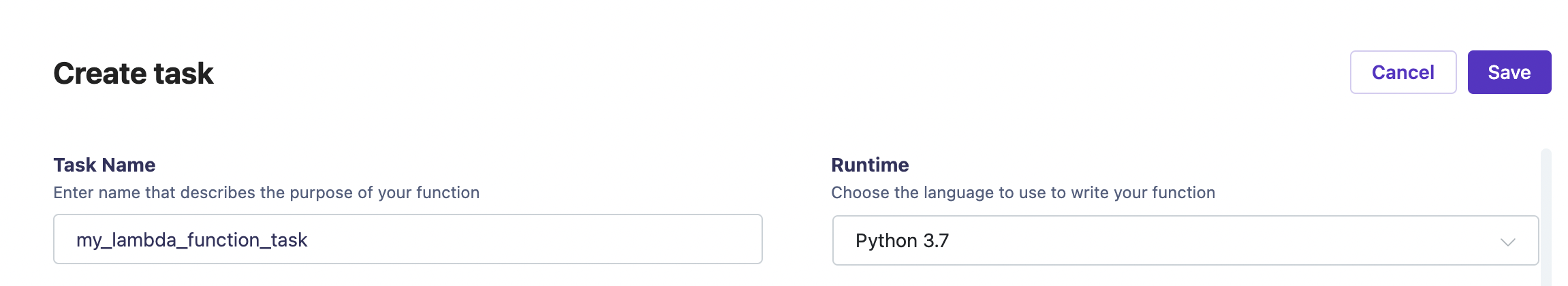
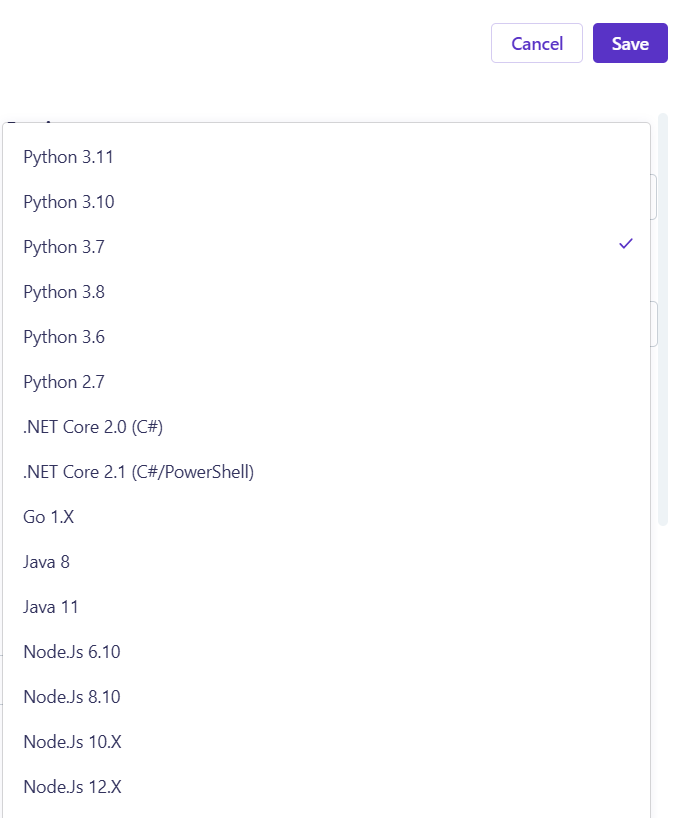
- Set Task Name and Runtime: Define your task name and select the appropriate runtime (e.g., Python 3.7).
You have to select the same runtime version as you used in your build. Version mismatch will cause errors!
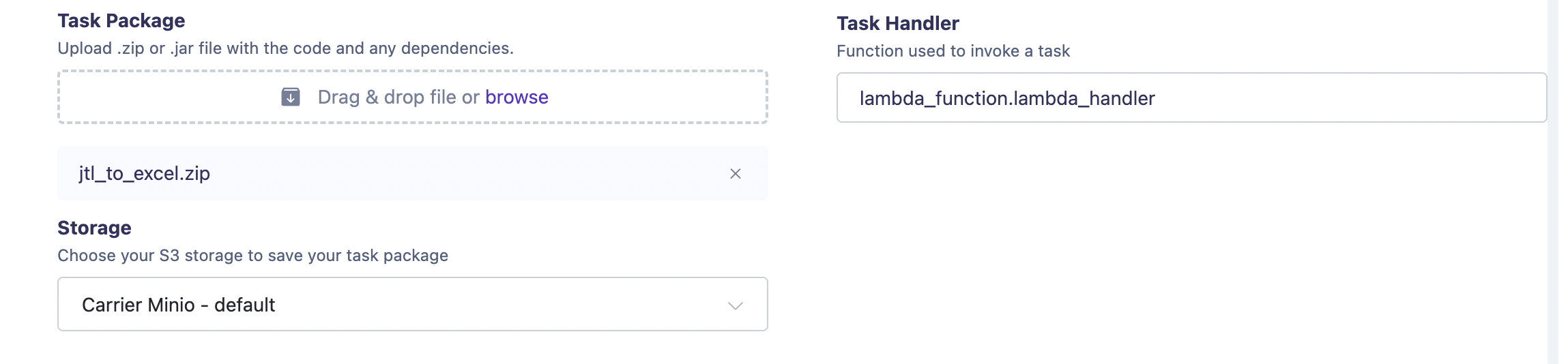
Upload Lambda Function: Upload the zip file containing your Lambda function and specify the Lambda handler.
![Tasks creation_part2]()
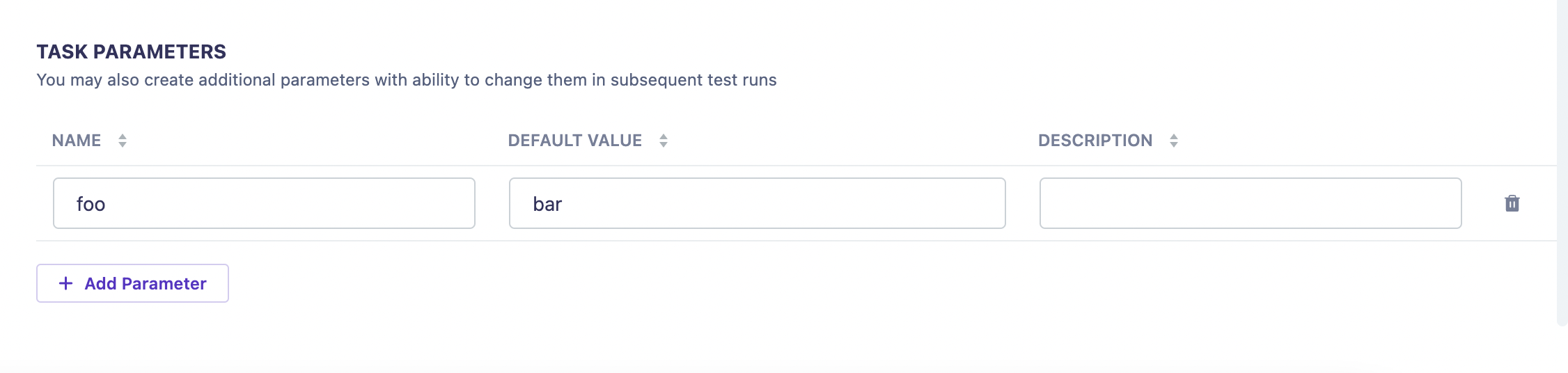
Configure Parameters: Add parameters that the Lambda function requires (e.g.,
report_id,project_id, etc.).![Tasks creation_part3]()
- Save and Execute: Save the task and execute it by selecting it from the task list and clicking the Play button.
![Tasks execution_part1]()
Carrier Tasks
By using Lambda tasks in Carrier, you can automate performance testing activities!
1. Explore Carrier’s task automation: Start by creating basic tasks, and then expand them with more complex scripts and integrations.
2. Measure the impact: Use the suggested KPIs and metrics to track improvements in your performance testing workflows.
3. Contribute: Explore how you can contribute new features and plugins to extend Carrier’s capabilities.
Self-learning
- Reporting Automation
- Use Case: Weekly or monthly report generation (e.g., performance results, Jira ticket summaries, comparison of test runs).
- Benefit: Automating reports reduces the manual effort spent gathering data, formatting it, and delivering insights to stakeholders.
- How to Measure: Calculate the time saved in report generation and the accuracy of automated reports. Track the reduction in manual reporting hours and faster access to results.
- Anomaly Detection in Test Results
- Use Case: Automated detection of response time spikes, throughput drops, and other anomalies in performance test results.
- Benefit: Early detection of performance issues reduces downtime and improves the stability of the system under test.
- How to Measure: Monitor how quickly anomalies are detected and resolved after automation. Track improvements in response times for identifying and fixing performance issues.
- Test Script Generation and Maintenance
- Use Case: Automate the generation of test scripts from HAR files or user flow diagrams, reducing time spent on script creation and updates.
- Benefit: Script automation ensures consistency and reduces manual errors in test script generation.
- How to Measure: Compare the time required for manual script creation versus automated generation. Track the number of new test scenarios covered.
- Integration
- Use Case: Seamlessly integrate custom logic in Jenkins, Azure, or GitHub Actions pipelines using Carrier tasks.
- Benefit: Automate performance testing setups and post-processing in workflows.
- How to Measure: Measure the reduction in setup times and consistency in test environments.
- Rescripting and Timeline Analysis
- Use Case: Automate rescripting tasks and create user-flow diagrams from test data to visualize the performance of specific flows.
- Benefit: Enables quick adjustments and optimization of user flows based on real-time performance data.
- How to Measure: Monitor how quickly user flows can be rescripted and optimized using automated tools.