Overview
This guide provides step-by-step instructions on how to configure CI for execution tests in Carrier. By running your test in CI you can check the performance of your application and identify any improvements or regressions.
Prerequisites
Before you begin, make sure you have completed the following:
- Installed and set up Carrier successfully
- Created a project in Carrier (Please find the configuration guides by following the link)
Steps
Follow the steps below to run tests in CI using Carrier:
Step 1: Log in to Carrier
- Open a web browser and enter the URL of your Carrier installation.
- Log in to the Carrier web interface using your credentials.
Note: Make sure you have logged in using the appropriate user account with access to the project where you want to configure the CI.
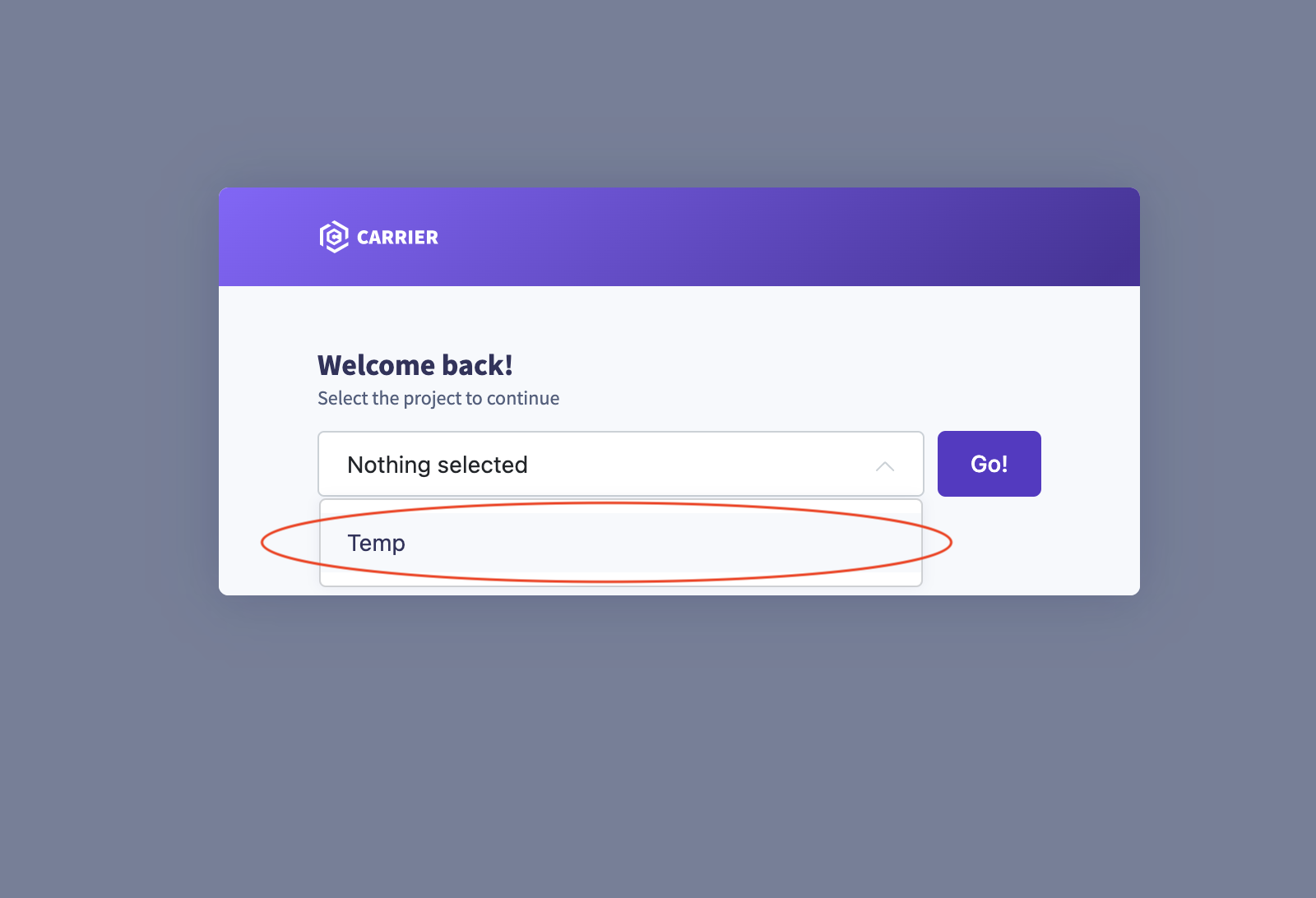
Step 2: Select the Project
- From the project dropdown menu, select the project you want to configure the CI for.
- Click “Go!” to navigate to the project’s configuration page.
![Select Project]()
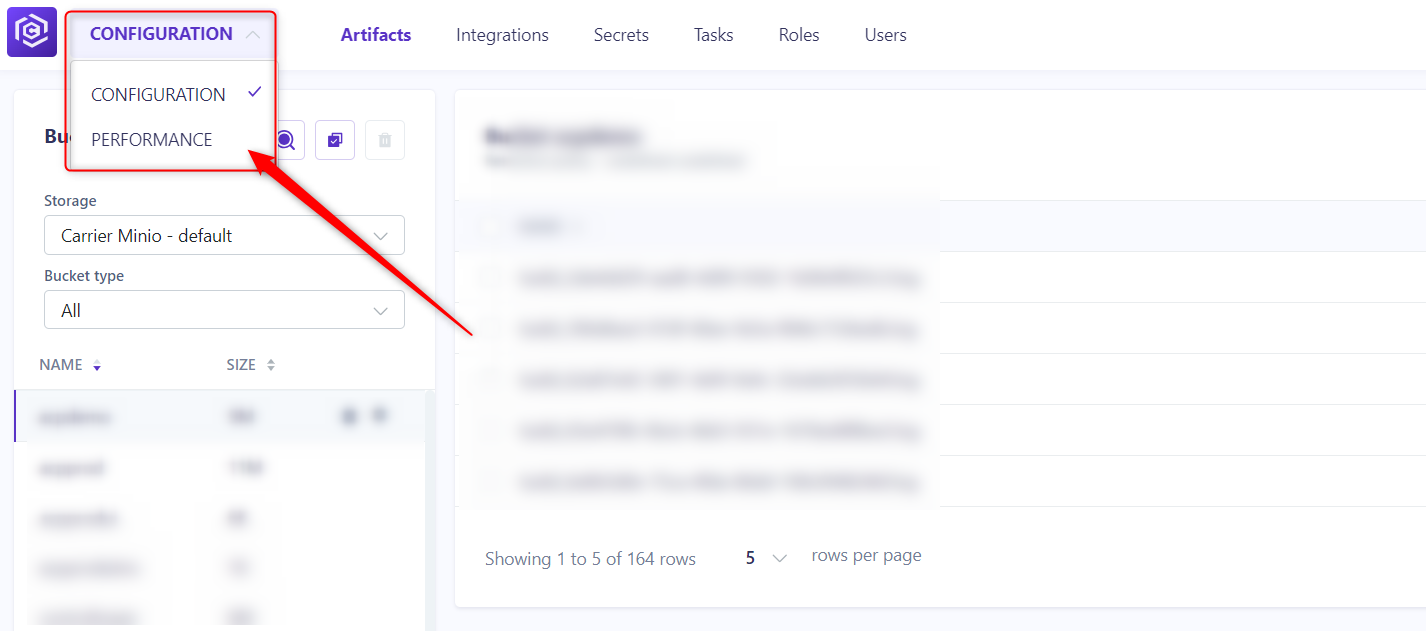
Step 3: Navigate to the “Performance” Tab
- On the project configuration page, click on the “Performance” tab located in the left menu.
![Performance Dropdown]()
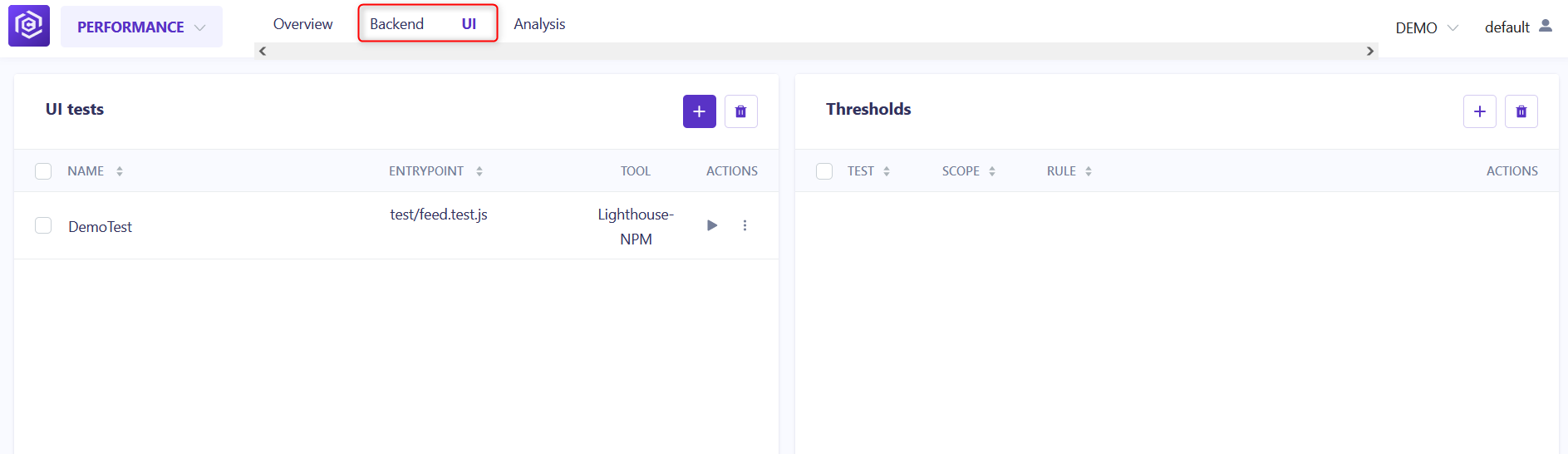
- Select the test type tab (
BackendorUI, depending on which test you configured before).![Navigate to Performance]()
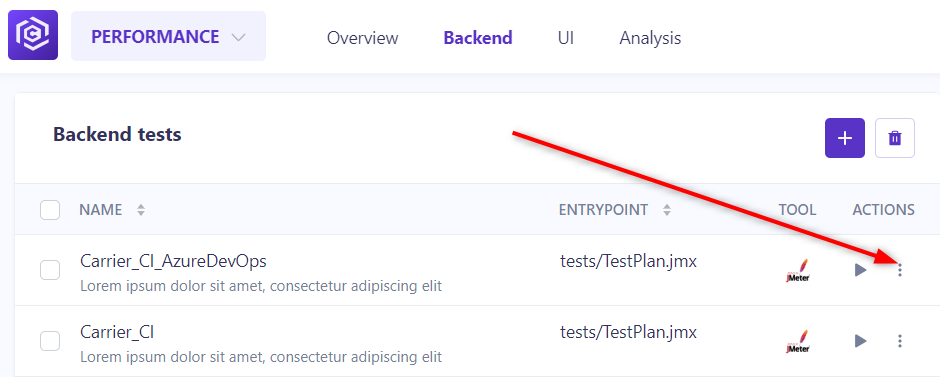
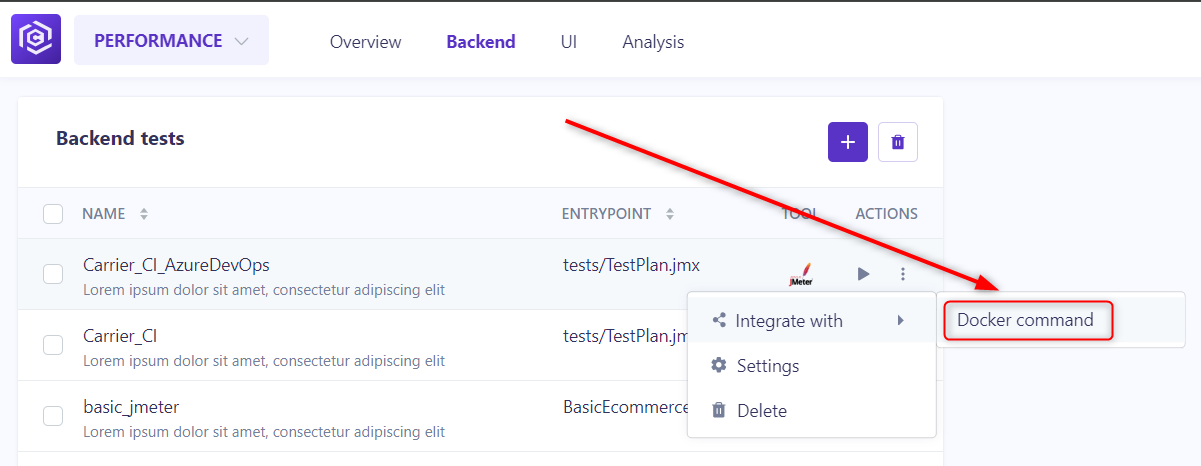
Step 4: Click on the more options button
- In your configurated test, click on the More options button (3 dots menu) tab located on the right of the test section.
![3 Dots Menu]()
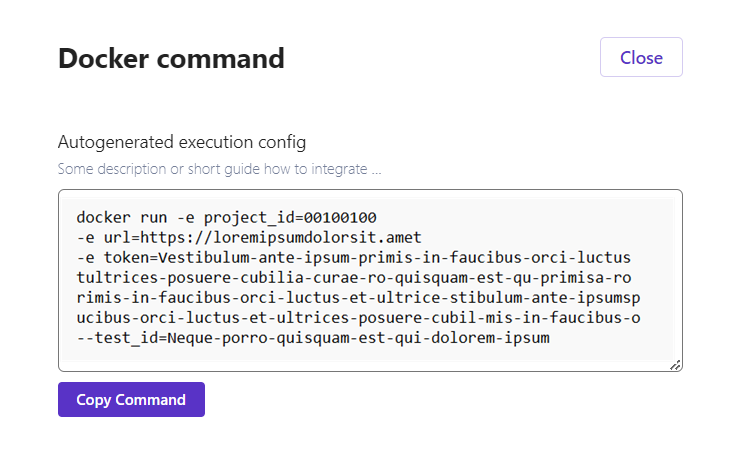
Step 5: Click on the Docker command button
Step 6: Click on the Copy Command button
Congratulations! Now you can use the copied command in your .yml files.
Step 7: Using Docker Command in .yml files
- Template of .yml file for GitHub Actions (Put your Docker Command on the line 31):
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
name: CI
# Controls when the workflow will run
on:
# Triggers the workflow on push or pull request events but only for the "main" branch
push:
branches: [ "main" ]
pull_request:
branches: [ "main" ]
# Allows you to run this workflow manually from the Actions tab
workflow_dispatch:
# A workflow run is made up of one or more jobs that can run sequentially or in parallel
jobs:
# This workflow contains a single job called "build"
build:
# The type of runner that the job will run on
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
# Steps represent a sequence of tasks that will be executed as part of the job
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v3
# Run the performance test using Carrier Docker container with the provided parameters
- name: Performance_Test
run: |
# Intercept test break to reset folder chmod
trap "sudo chmod -R 777 $GITHUB_WORKSPACE" SIGINT SIGTERM SIGKILL
# PUT YOUR DOCKER COMMAND ON THE LINE 31 BELOW \/ \/ \/
sudo chmod -R 777 $GITHUB_WORKSPACE
- Template of .yml file for AzureDevOps Pipelines (Put your pool name on the line 7 and your Docker Command on the line 28):
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
trigger:
- main
stages:
- stage: Server_Side
pool:
name: #PUT YOUR POOL NAME HERE
dependsOn: []
displayName: Performance_Test
jobs:
- job: PerfTest
variables:
timeoutInMinutes: 810 # Set a timeout of 810 mins to cancel the job automatically if it exceeds the limit
displayName: PerfTest
steps:
# Run the performance test using Carrier Docker container with the provided parameters
- task: Bash@3
displayName: Run Test
inputs:
targetType: 'inline'
script: |
# Intercept test break to reset folder chmod
trap "sudo chmod -R 777 $(Build.SourcesDirectory)" SIGINT SIGTERM SIGKILL
# PUT YOUR DOCKER COMMAND ON THE LINE 28 BELOW \/ \/ \/
sudo chmod -R 777 $(Build.SourcesDirectory)
- Template of .yml file for GitLab Pipelines (Put your Docker Command on the line 13):
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
stages:
- test
lint-test-job:
stage: test
image: docker:19.03.12 # Use an image that has Docker installed
services:
- docker:19.03.12-dind # Enable Docker-in-Docker
before_script:
- docker info # Verify Docker was correctly installed
script:
- trap "sudo chmod -R 777 ${CI_PROJECT_DIR}" SIGINT SIGTERM SIGKILL
- # PUT YOUR DOCKER COMMAND HERE
- chmod -R 777 "${CI_PROJECT_DIR}"